Cryptography
What is Kerberos?
Cryptographyis the science of secret writing with the intention of keeping the data secret. Cryptography is classified into symmetric cryptography, asymmetric cryptography and hashing.
[Kerberos] in Greek mythology was a three-headed hound of Haides.
Kerberos is a protocol for authenticating service requests between trusted hosts across an untrusted network, such as the internet. Kerberos is built in to all major operating systems, including Microsoft Windows, Apple OS X, FreeBSD and Linux.
Parties Involved:
- Client
- Server
- Key distribution center(KDC)
KDC is made up of:
- AS – > Authentication server.
- TGS – > Ticket Granting server.
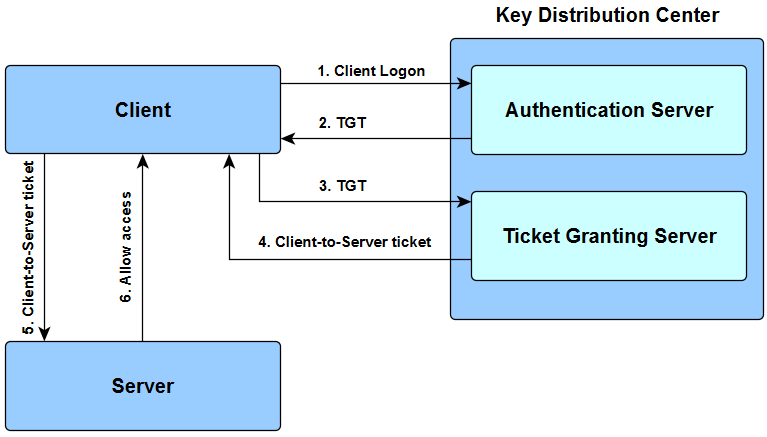
- Client sends a request to the AS along with their server credentials. The whole message is encrypted using a secret key which is the client’s password.
- AS looks for the client’s credentials in its database and uses client’s password to decrypt the request.
- After authenticating the client, AS send a TGT (ticket granting ticket) to the client which is encrypted with a another secret key.
- Client forwards the TGT to the TGS along with their request such as “I want to access the file server”.
- TGS decrypts the request with the secret key shared by AS.
- TGS issues the client with a token encrypted with another secret key which is shared with the File server.
- The client forwards the service token to the file server.
- The file server decrypts the service token with a key shared by TGS if the decryption is successful, it allows the client to use its resources for a certain period of time as indicated in the token.
This method of authentication is called Symmetric cryptography.
Private key Cryptography / Symmetric Encryption
In Private key encryption: Data is encrypted using a single key known only to the sender and receiver. Private key encryption is also called symmetric encryption / cryptography, because a single key is used in both encryption and decryption.
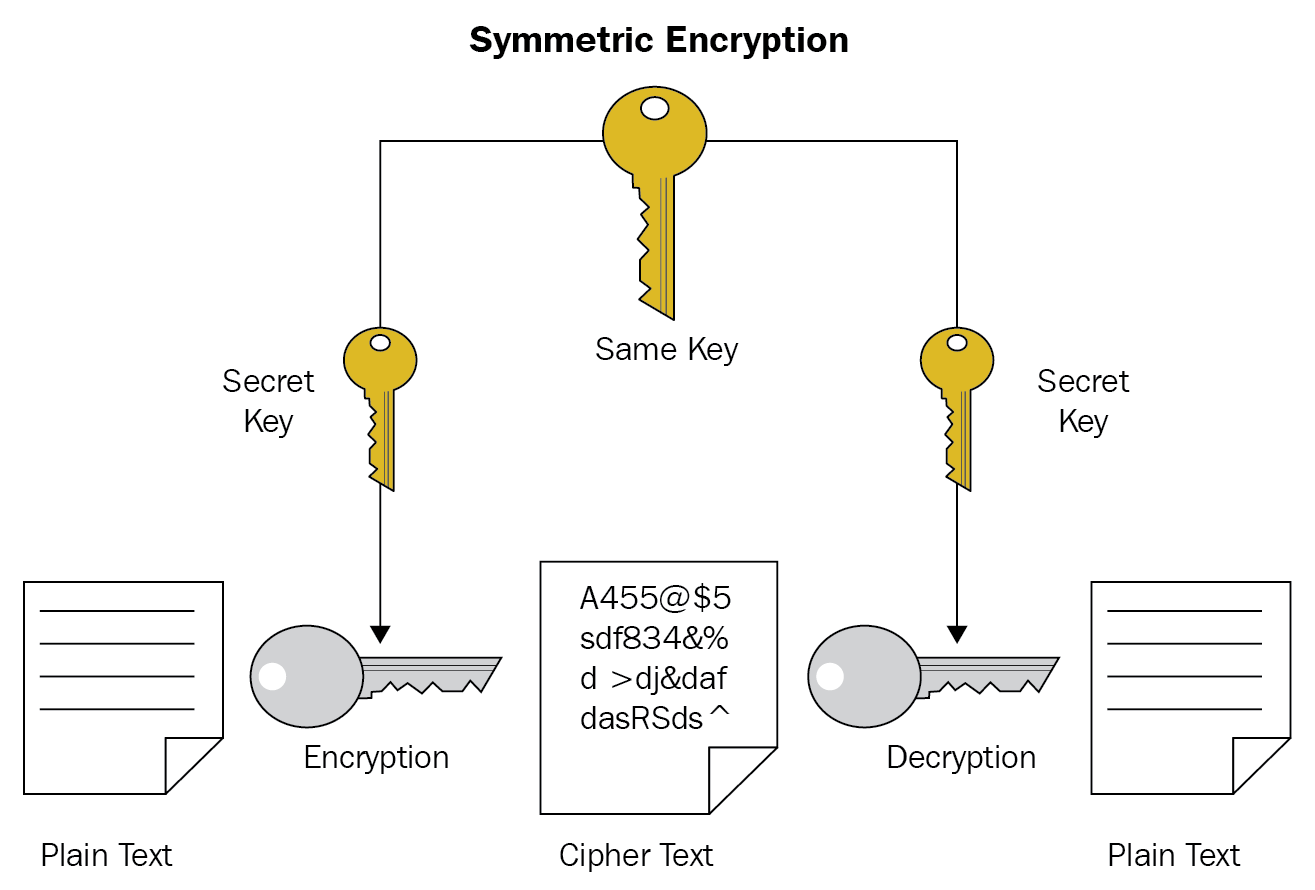
Private key encryption methods:
- Stream ciphers — > works on a single bit at a time.
- Block ciphers — > operates on a fixed block of bits, data comes in chunks.
An example:
- AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
The biggest problem with this cryptography method is that the sender needs a way of sharing the private key with the receiver.
If someone was to get his hands on the secret key, that person will be able to decrypt any info sent between the two parties.
Public key Cryptography / Asymmetric Encryption
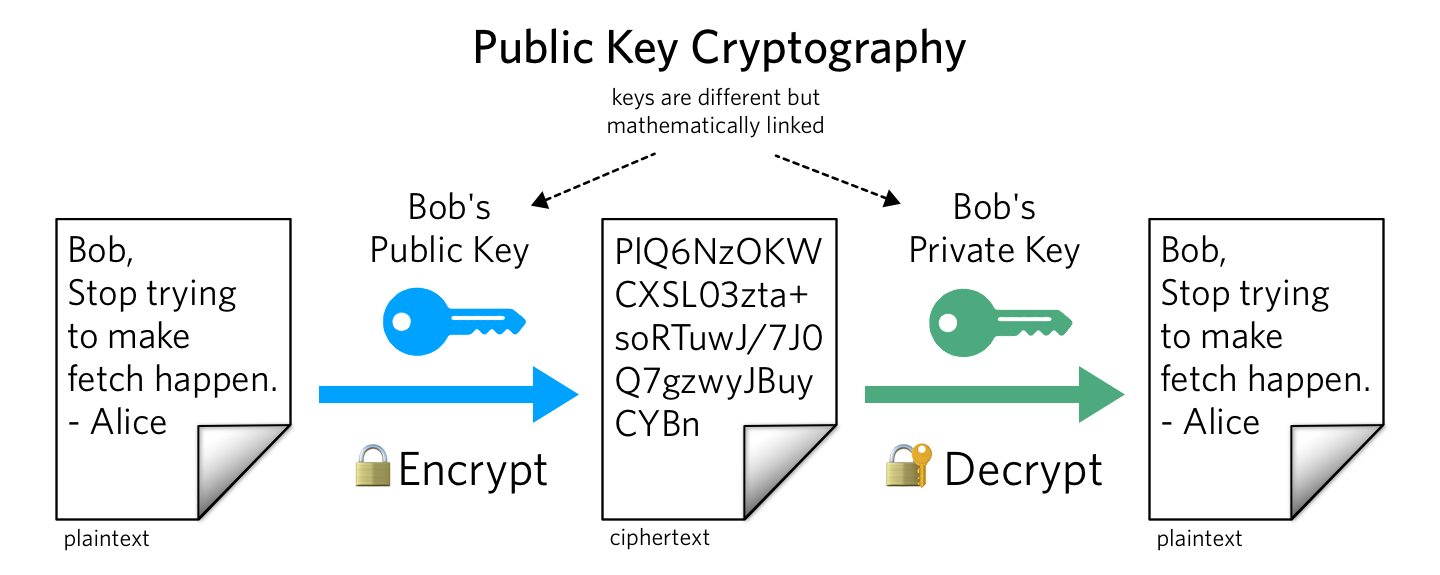
Public key cryptography uses two keys. One key (public key) is used for encryption while the other key (private key) is used for decryption. The public key is used to encrypt a plain text and convert it into a cipher text while private key is used by the receiver to decrypt the cipher text and read the message.
The encryption process starts with the receiver
- The receiver creates a pair of keys, a private and a public. The receiver keeps the private key and sends the public key to the sender.
- The sender encrypts their message with the public key
- The receiver gets the message and decrypts it using the private key.
The problem is the receiver can’t verify who really sent the message. In order to verify the sender needs a digital signature




Leave a comment